Diabetic Wounds

Diabetes is a result of your body’s inability to produce or use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows your body to turn glucose, or sugar, into energy. If your body has difficulty metabolizing glucose, it can lead to high blood sugar levels. This can affect your body’s ability to heal wounds.
In people with diabetes, wounds tend to heal more slowly and progress more quickly, so it’s important to know what to look out for.
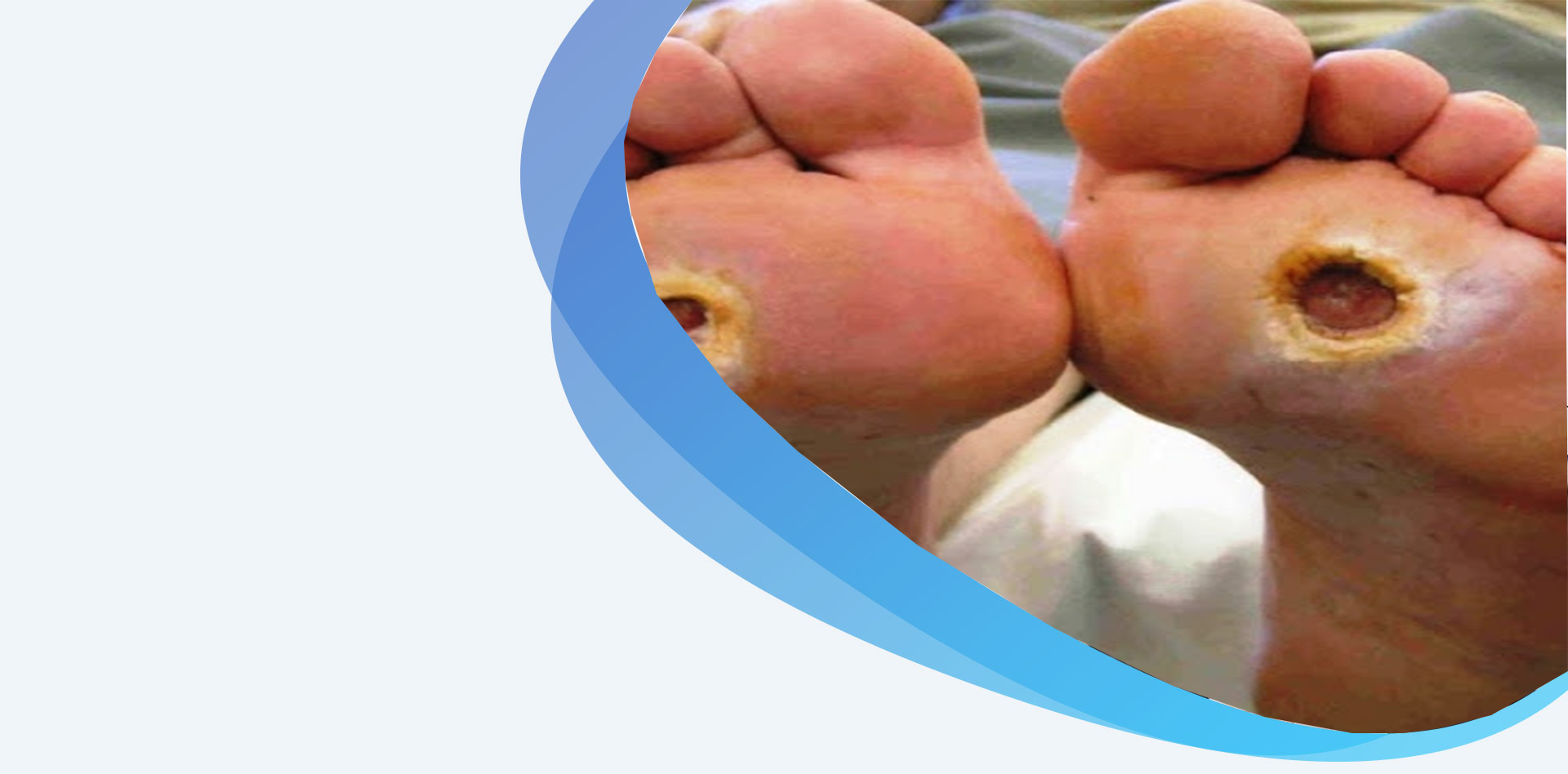
Although cuts, grazes, scratches, and blisters can occur anywhere on the body, the feet are one of the most common places of injury. A small wound on the foot can quickly develop into a foot ulcer.
Foot ulcers can become serious if left untreated. Between 14 and 24 percent of people who have diabetes and develop an ulcer will end up having a lower limb amputation.
For this reason, it’s crucial that you do regular self-checks and closely monitor any wounds closely. Catching wounds early is the only way to reduce your risk of complications.
Keep reading to learn more about the healing process, ways to speed the healing process along, and how to improve your body’s healing powers long-term.
When you have diabetes, a number of factors can affect your body’s ability to heal wounds.
Your blood sugar level is the main factor in how quickly your wound will heal.
When your blood sugar level is higher than normal, it:
These effects slow down wound healing.
Peripheral neuropathy can also result from having blood sugar levels that are consistently higher than normal. Over time, damage occurs to the nerves and vessels. This can cause the affected areas to lose sensation.
Neuropathy is particularly common in the hands and feet. When it happens, you may not be able to feel wounds when they occur. This is one major reason why foot wounds tend to be more common in people with diabetes.
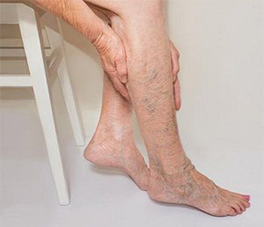
People with diabetes are twice as likely to develop peripheral vascular disease, a condition of poor circulation. Peripheral vascular disease causes your blood vessels to narrow, which reduces blood flow to the limbs. The condition also affects red blood cells’ ability to pass through the vessels easily. And a higher-than-normal blood glucose level increases the thickness of blood, affecting the body’s blood flow even more.
Many people who have diabetes also have problems with immune system activation. The number of immune fighter cells sent to heal wounds, and their ability to take action, is often reduced. If your immune system can’t function properly, wound healing is slower and your risk of infection is higher.
If your immune system isn’t functioning at its best, your body may struggle to fight off bacteria that cause infection.
Higher-than-normal blood sugar levels also increase the possibility of infection. This is because bacteria thrive on the extra sugar that’s available in the bloodstream. High blood sugar levels can also prevent immune cells from being able to fight off invading bacteria.
If your infection is untreated and left to spread, it can lead to complications such as gangrene or sepsis.
Wounds present a real cause for concern. If they’re not carefully monitored, they can quickly progress into an infection or more serious complication.
The most serious concern is amputation. People with diabetes are 15 times more likely to have amputations as a result of foot wounds or ulcers.
Treatment of Diabetic Wounds is a very specialised are and a large majority of patients end up spending thousands of rupees getting sub-standard treatment without proper evaluation of the critical concepts in wound healing in the setting of Diabetes.
The following factors are very critical in satisfactory outcomes and in the prevention of loss of limb or life due to accelerating infections.
The extraordinary success rate of wound healing at our Clinic is due to the multi-disciplinary approach undertaken and the scientific method of wound assesment.
On your first visit you shall undergo a wound mapping and basic lab investigations to asssess the infective load and antibiotic treatment plan shall be initiated.
Based on the complexity of the wound you may have to undergo vascular assesment as more than 80% of all diabetic wounds have poor blood supply in the affected limb and hence all forms of therapy fail unless the limb is revascularised.
The Clinic used advanced dressing straytegies such as VAC, HBOT, Custom Dressings and we have an able quorum of experienced PLastic Surgeons/Gen Surgeons/Orthopeditians who will undertake the necessary surgical work to clean and debride badly infected complex wounds.
Our Dietitians will help you plan a pro-anabolic diet to promote wound healing and optimise blood sugar control.

If you’re dealing with a foot wound, consider wearing white socks during the healing process. This will make it easier to see blood or other signs of drainage on your socks.
See your doctor if you experience any of the following:
You should also see your doctor if your symptoms worsen or last longer than a week.
Any break in the skin of your feet is cause for concern, so if you’re unsure about the wound, see your doctor. They can identify the wound and advise you on how best to care for it. The faster you get the appropriate treatment, the more likely you are to prevent complications.

There are a few things you can do to boost your immune system and aid in wound healing.
Eat a healthy diet. Diet has a direct influence on blood sugar levels, so maintaining proper nutrition is key. If you can consistently maintain healthy glucose levels, you’re more likely to avoid wounds and heal faster should a wound occur.
People with diabetes can often maintain better blood sugar control by avoiding processed carbohydrates, added sugars, and fast food. It also helps to increase your intake of fiber, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Good nutrition provides what your body needs for faster wound healing, such as vitamin C, zinc, and protein.
Stay active. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity. This helps sugar in the bloodstream enter your cells more efficiently, which promotes healing and health.
Quit smoking. Smoking decreases your cells’ ability to carry oxygen. Smoking also disrupts the immune system and increases your risk of vascular disease.