Transcarotid Artery Revascularisation
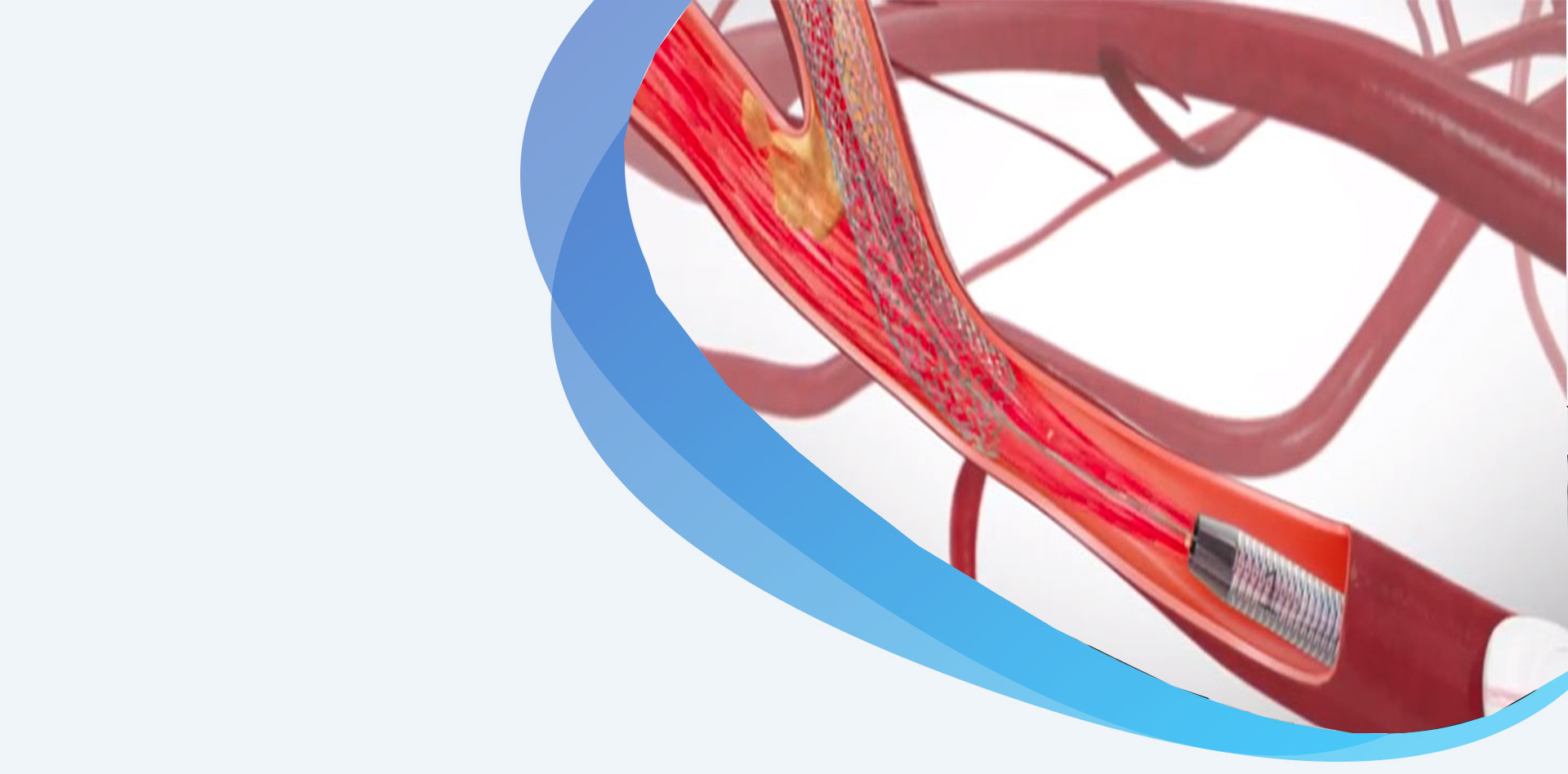


Transcarotid Artery Revascularization (TCAR) is a clinically proven, minimally invasive procedure to treat carotid artery disease and help prevent future strokes. TCAR is unique in that blood flow is temporarily reversed during the procedure so that any bits of plaque that may break off are diverted away from the brain.

Your vascular surgeon may recommend a TCAR procedure if:

The TCAR procedure takes place in an operating room. Local or general anesthesia may be used – your surgeon will determine what is best for you.
While any intervention of the carotid artery carries some risk of causing a stroke because of the procedure itself, TCAR was designed to help minimize that risk. Potential risks of TCAR include:


Patients who undergo the TCAR procedure recover quickly, typically spending just one night in the hospital. Before you leave the hospital, your doctor will give you advice for activity, diet and medications.