Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
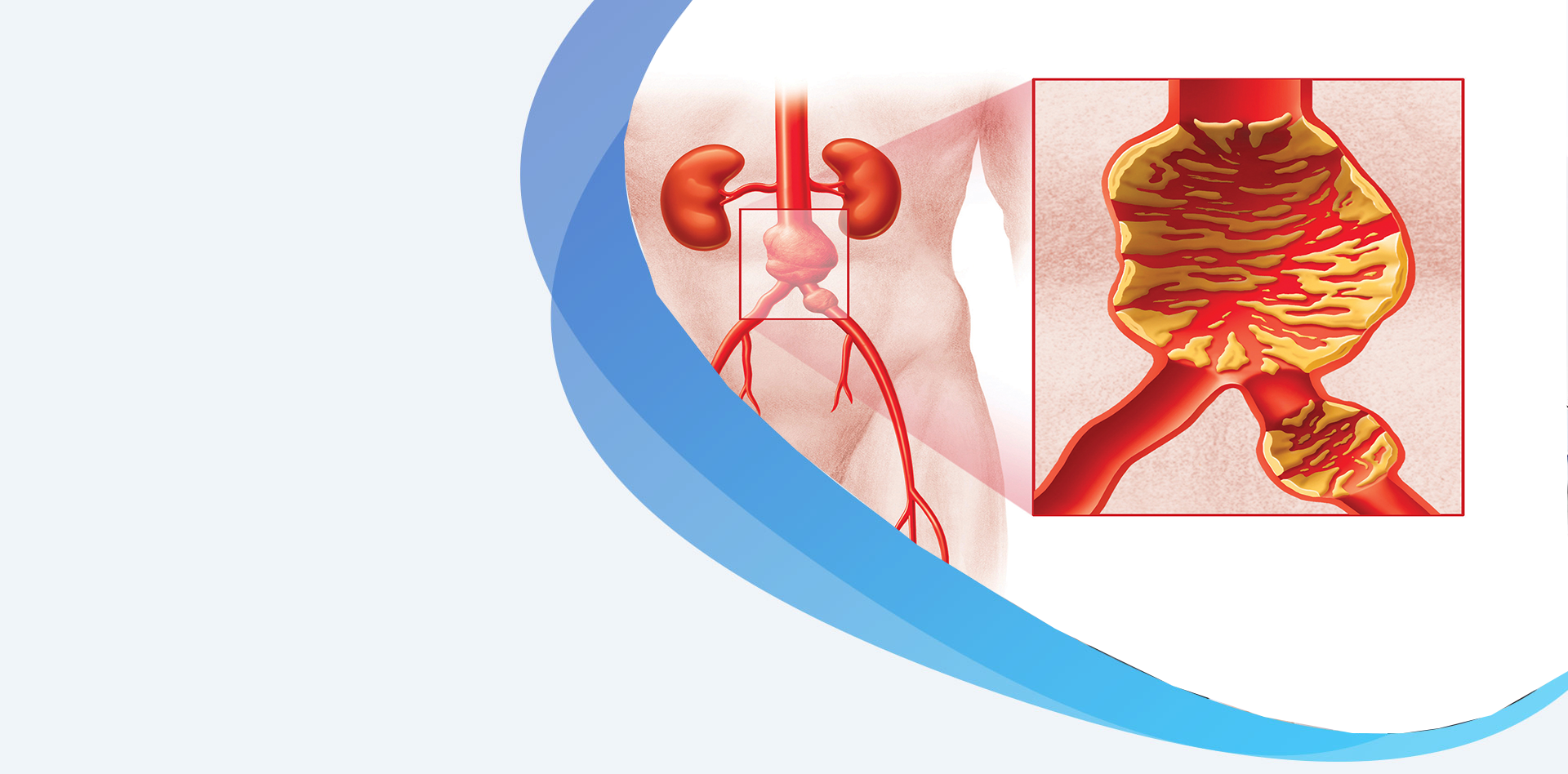

When the wall of a blood vessel weakens, a balloon-like dilation called an aneurysm sometimes develops. This happens most often in the abdominal aorta, an essential blood vessel that supplies blood to your legs.
Every year, over 2 lakh people are diagnosed with an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA).
A ruptured AAA is the 15th leading cause of death in the country, and the 10th leading cause of death in men older than 55.
Aneurysms run in families. If a first-degree relative has had an AAA, you are 12 times more likely to develop an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Of patients in treatment to repair an AAA, 15–25% have a first-degree relative with the same type of aneurysm.
In most cases, abdominal aortic aneurysms cause no symptoms and are found when you are being evaluated for another medical condition.
If you have a family history of AAA and feel sudden, severe pain in your abdomen or back, seek immediate care. These symptoms may signal that you have developed an AAA, possibly one in process of rupturing.
A small percentage of patients with AAA have these symptoms when plaque or blood clots from elsewhere in the body collect in the feet and toes.
Many factors contribute to AAA formation.
Most AAAs cause no symptoms and are found incidentally, during an evaluation for another medical condition. If you are affected, see a vascular surgeon.
An abdominal ultrasound is painless, cost-effective, safe and the most frequently utilized test to screen for and measure the size of an AAA.
Computerised Tomographic Angiography (CTA) will assess aneurysm size, location and the extent of impact. This study requires exposure to radiation and injection of an intravenous contrast agent. However, a CTA provides valuable anatomic information and can help your vascular surgeon determine the optimal type of repair.
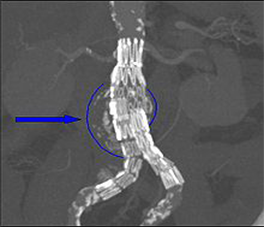
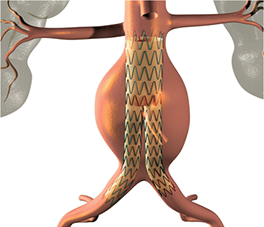
Treatment depends on the size of the aneurysm.
have a very low risk of rupturing, but should be watched.
rapidly enlarging and AAAs causing symptoms are usually repaired.
Open surgery requires placement of a prosthetic graft.
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a less invasive treatment.